1. Scan Tool Data
1.1 Find a vehicle which is appropriate for the scan tool.
1.2 Connect the scanner, power it on, follow the instructions and input the correct vehicle information it asks for so you can view the data.
1.3 Find the data for the information listed on the next page. Turn engine on to idle. Fill in the letters used to label the information and the value of that data. (For example, engine load information may be found under MAP, with a value of 3.6, listed in volts) Note: not all vehicles will support all information, just find as much as you can. If the engine won’t run, input the information with the key on, engine off.
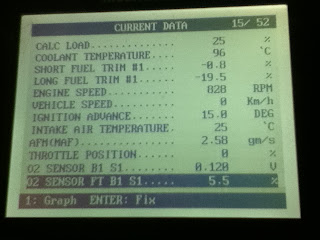
| Type of information (PID = Parameter Identification) | Letters to describe it E.g. TPS | Value of data | Units for data E.g. volts |
| Engine Load (how much air comes in) | AFM(MAF) | 2.58 | gm/s |
| Engine RPM | Engine Speed | 695 | RPM |
| Throttle angle | TPS | 11 | % |
| Engine coolant temperature | Coolant Temperature | 89 | C |
| Intake air temperature | Intake air Temperature | 21 | C |
| Fuel Injection opening pulse | Injector Pulse Width | 2.6 | mS |
| Transmission select position | Shift | 4 | |
| Vehicle Speed | 0 | 0 | km/h |
| Oxygen sensor(s) | O2 Sensor B1 S1 | 0.375 | V |
| Fuel Trim | Short Fuel Trim#1 | -2.3 | % |
| Idle control | IAC Duty ratio | 37.5 | % |
| Power steering condition | PS Signal | OFF | |
| Air conditioning condition | A/C cut signal | ON | |
| Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) | |||
| Fuel Evap or Purge condition | EVAP VSV | OFF | |
| Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) | Warning Light/MIL | OFF | |
| Barometric Pressure |
2 Trouble Codes or Fault Codes
2.1 Find where the Codes are listed
2.2 Record any codes, and what system and condition they describe in the chart below Example: might be code number 21, for Throttle Position Sensor, signal voltage too low) If there are no codes listed, put “none”.
3 Lecturer put in Fault
3.1 Find your lecturer and have him create a fault under the hood (don’t look)
4 Record New Codes
4.1 Look up the codes now in the scan tool
4.2 Record the codes in the chart below. Also record what system is affected, and what condition is described.
The Faulty code P0120 TPS circuit malfunction.
5 Find What Data Has Changed
5.1 Look through the scan tool data to see what PIDs
(Parameter Identification of system voltages) have changed.
Which readings don’t make sense or don’t read what you would expect. Concentrate on the PIDs related to the codes.
The throttle position is 0% which means scan tools proof it.
6 Visual Inspection to find fault
6.1 Do a visual inspection under the hood to find where the problem is. Use information from the code to know where to look for the problem and what type of problem to look for.
Describe problem you found:
Obviously there was not problem.
7 Repair fault
7.1 Plug back in the connector, or repair problem found
7.2 Describe what you did:
We can check by multi-meter, related to the TPS wires terminal from voltage reference, signal and grounding.
8 Clear Codes
Recheck the code
The Faulty code P0120 TPS circuit malfunction did not come up again.
Discuss the importance live data when fault finding
Live data very important to trace and track the faulty on time so we can fix the problem straight away.
Explain the need for parameters when checking live data
Off course we need the parameter when using the scan tools for identify which is faulty one. Wrong parameter or reading causing make another problem.
Discuss how a scan tool can aid you when fault finding
The scan tools will telling us what the problem is from ECU and must remember scan tools is not perfect magic tools, sometimes scan tools read not exactly what the problem is but close to the faulty. In the car consist of several section, in each section there is few sensor, they are communicate each other for a reason.










No comments:
Post a Comment